What is waterjet cutting?
Effective cutting process with high precision and quality
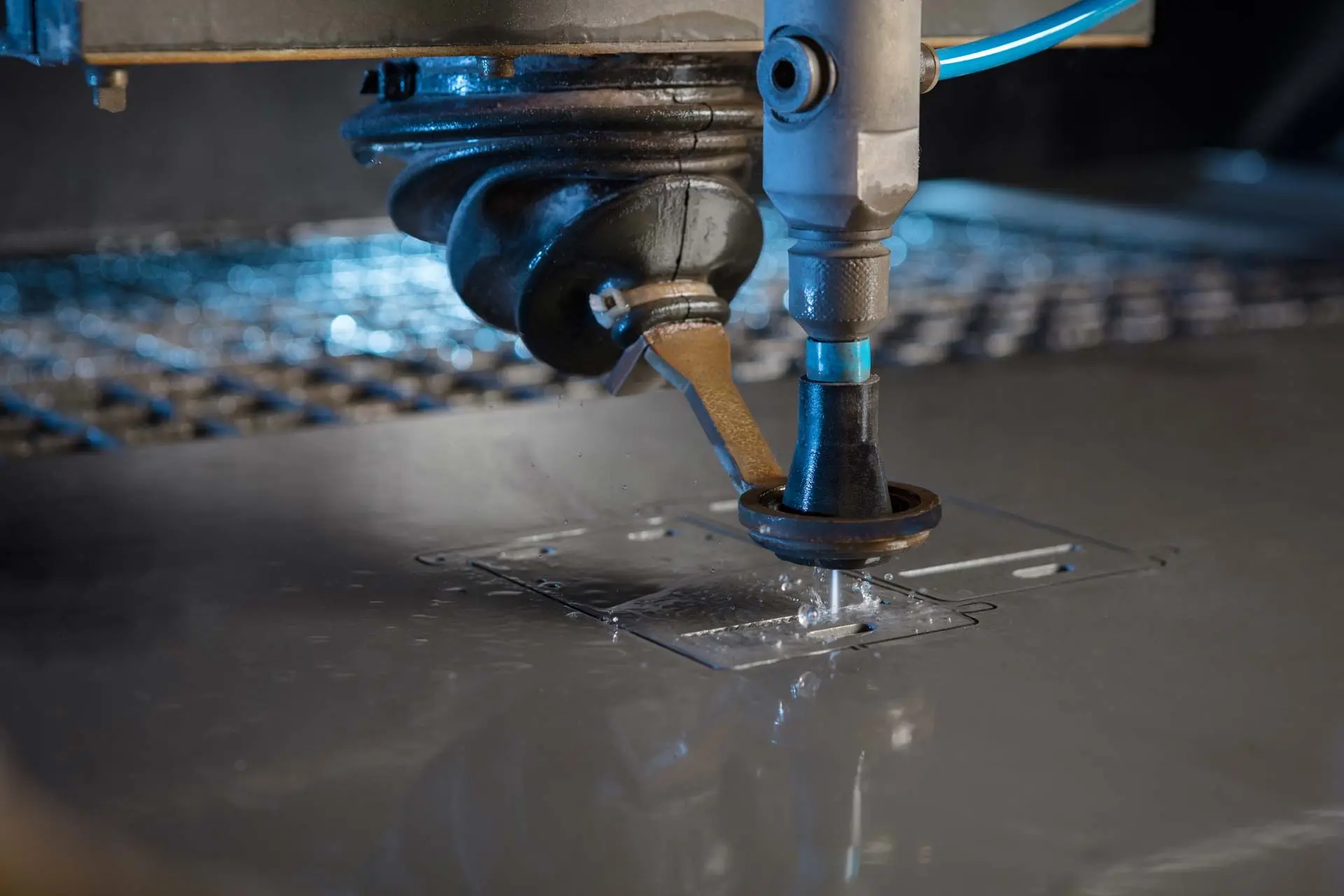
Waterjet cutting is an effective method for cutting materials of different types and thicknesses. More precisely, it is a cutting process (cold cutting process) with high precision and quality. In waterjet cutting, a basic distinction is made between pure waterjet cutting and abrasive waterjet cutting.
Table of contents
Table of contents
History
A brief excerpt from the history of waterjet cutting
Water jets were used in mining in the early 20th century to remove gravel or clay deposits. In California’s gold mines, it was used to separate gold veins from rocks and soil.
-
1930
From 1930, American and Russian engineers used it for fettling castings. At that time, pressures as low as 100 bar were used.
-
60s
In the late 1960s, it was used in the aircraft industry to separate parts that are sensitive to heat such as fiber composites, honeycomb and laminated materials.
-
1974
From 1974, hard particles were used as an additive in the waterjet, which significantly increased the quality of the workpieces and the cost-effectiveness of the process, leading to its breakthrough in industrial application.
-
1975/76
In 1975/76, building materials, plastics and corrugated board were separated using the process.
-
Current
In the meantime, the technology has developed greatly and there are many more possibilities and fields of application.
Source: Wikipedia
How does waterjet cutting work?
In waterjet cutting, a workpiece is separated by a high-pressure water jet. Either filtered water or an abrasive (e.g. sand) is used in addition to the water. In this process, the water jet separates superficial and microscopic particles.
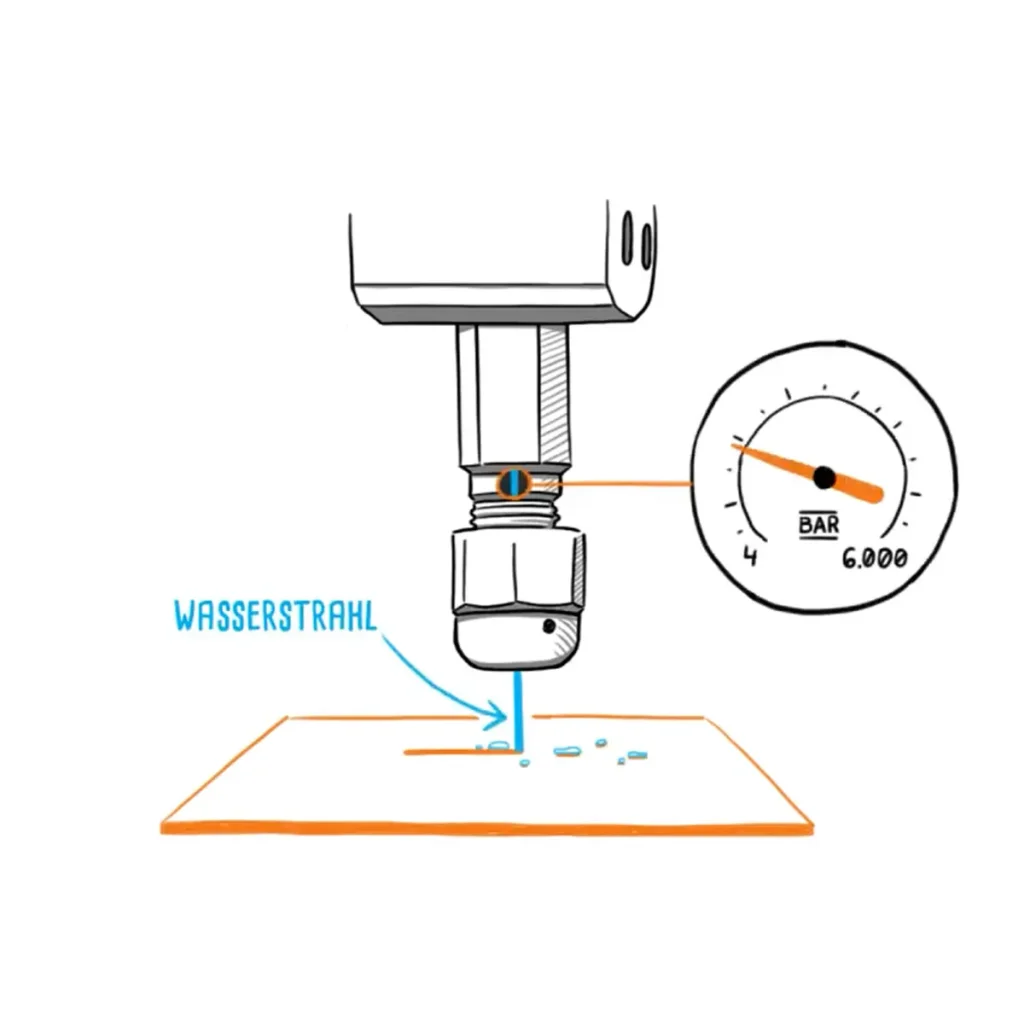
- Pressure generation
A high-pressure pump is used to generate a water jet with a pressure of 3500-6000 bar. (e.g.: operating pressure of a fire hose is approx. 17 bar)
- Beam generation
This jet of water is forced through a nozzle. This produces a thin jet with 2-3 Mach (air-sound velocity).
- Abrasive
In order to increase the cutting force by a factor of 1000 for harder materials, sharp-edged cutting sand (abrasive) is added.
Cold cutting is a cutting process that works without the application or generation of heat, which is why it is called “cold”.
Waterjet cutting does not lead to heating or thermal deformation of the material. The cut material usually remains in its original shape and does not change its original properties.
Water quality is important to ensure optimal performance.
It is important that the water is clean and free of impurities to ensure that the waterjet cutting system functions properly. Therefore, filtration and purification systems are usually used to treat the water in the best possible way.
The water pressure for waterjet cutting is 3500 – 6000 bar. Thanks to the high pressure, the water jet is able to penetrate the material and cut through it precisely.
The cutting speed depends on the material, thickness, desired accuracy of the cut.
As a rule, this is set so that the required cutting quality is achieved at high feed rates in order to make the cutting process as efficient as possible
The cutting speeds are mostly between 500 – 4000 mm/min. However, they can also be significantly lower (fine cuts for metals) or higher (plastics and foams).
Waterjet cutting is characterized by high cutting quality.
There is no heat influence, so there is no heat discoloration or deformation of the material. The cut edges are clean and precise, without burrs or chipping. The process enables cutting of complex shapes and tight curves with high accuracy.
Waterjet cutting explained quickly and simply
Waterjet cutting explained in 90 seconds.
You will learn in a short time how waterjet cutting works and what makes it so special.
We also explain how our machines and SmartCut cutting software make your job easier.
Did you know?
The process of waterjet cutting with pure water is particularly environmentally friendly. The water here can be recycled and reused with relatively little effort.
Water jet techniques
With waterjet cutting, as already mentioned, many different materials can be cut. The desired results differ in form and structure. Therefore, there are different waterjet techniques to cut small and fine materials as well as complex three-dimensional shapes.
There are 3 main types of waterjet techniques: 2D, 3D and Microcutting.
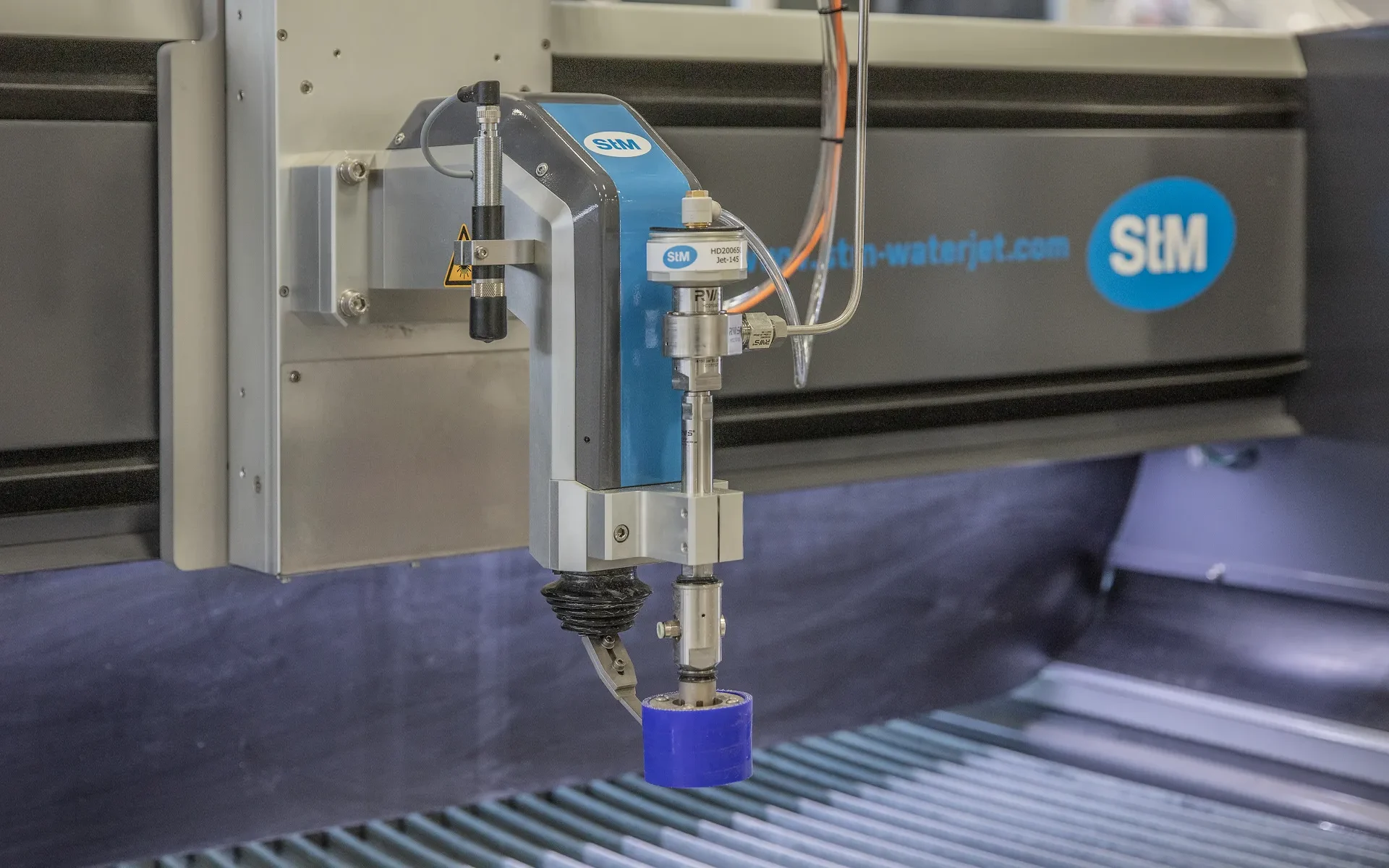

2D cutting
With 2D cutting, or 2D cutting, is the cutting of two-dimensional materials.
In this specialty, the waterjet is used to make precise cuts in a plane. Complex shapes and contours are cut into flat materials.
Typical applications for 2D cutting are cutting metal sheets, plastic sheets, rubber, paper and other materials.
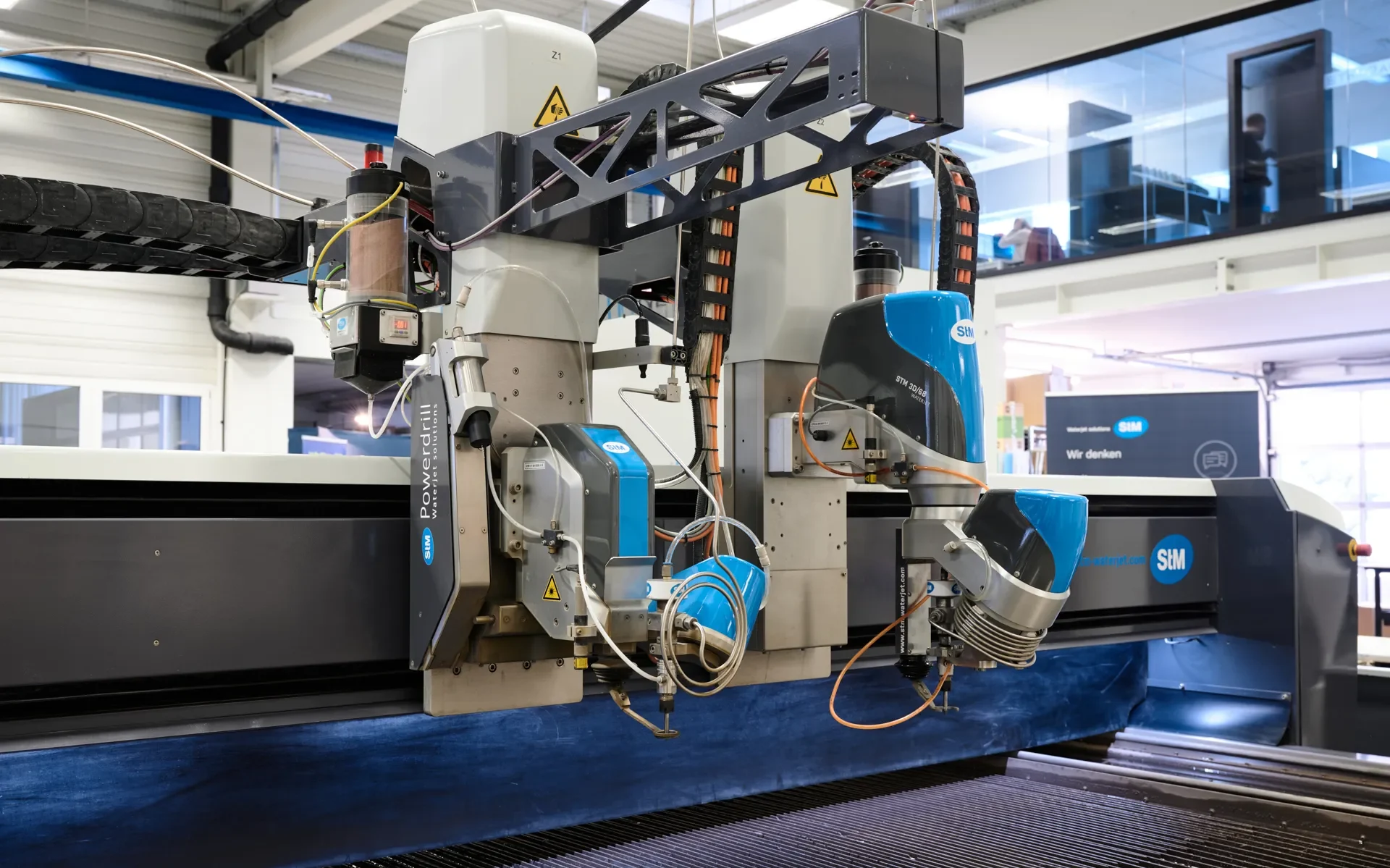

3D Cutting
3D cutting, or 3D cutting, refers to the cutting of complex three-dimensional, structures.
This technique uses a waterjet to make angled cuts in multiple planes or angles to produce three-dimensional shapes, such as 45° chamfers.
3D cutting is ideal for creating prototypes, artwork and sculptures from materials such as foam, composites, stone and metal.

Micro-Cutting
Microcutting, or microcutting, is the term used when cutting very small & fine contours.
Special nozzles and fine abrasives are used to make tiny cuts in materials such as semiconductors, microchips, implants and fine metal parts.
Microcutting is used in micromechanics, microelectronics, medical technology and other high-tech industries where high precision and accuracy are required.
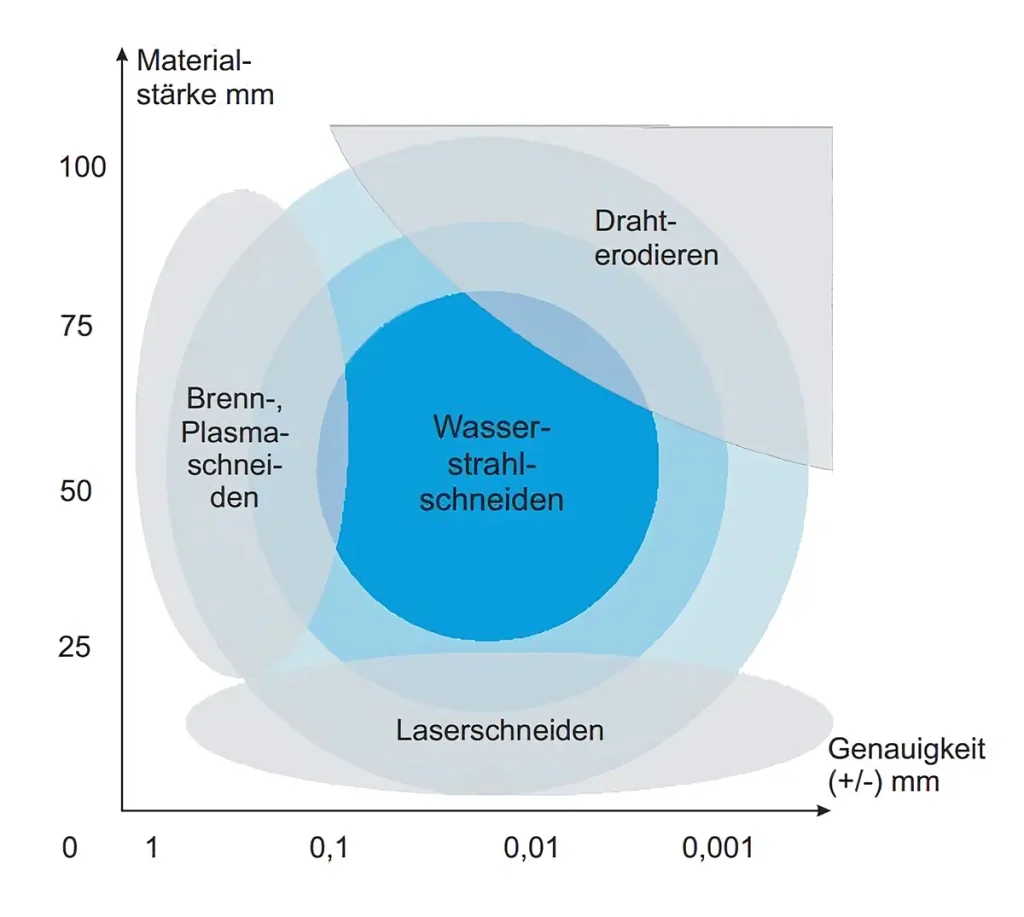
Can waterjet cutting be used to separate all materials?
Waterjet cutting works with almost all materials up to 300mm material thickness.
Waterjet cutting is extremely versatile and can cut a wide range of materials including metal, plastic, stone, glass and composites. For soft material, cutting with pure water is sufficient. For harder materials, so-called abrasive sand is added.
The working areas of our waterjet cutting systems range from 1m x 1m(STM Cube) to 6m x 16m(STM PremiumCut IFC). However, the unique STM modular system for waterjet cutting systems stands for maximum flexibility and enables each customer to find a tailor-made solution in the desired machine size. Special systems, beyond these sizes listed here are possible on request!
At STM, we focus on your cutting requirements and offer you a customized solution for pure water or abrasive waterjet cutting of your material. Feel free to contact us or request a test cut with your material.
Types of waterjet cutting
Pure water cutting
A gentle separation process for soft materials
In pure water cutting, soft materials are cut through exclusively with water, at a speed of Mach 2. This includes cutting foams, rubber, insulating materials, foils, felt, cork, gaskets, wood or and many other soft materials.
Another special feature of pure water cutting of plastics and foams is that even cutting thicknesses of over 300 mm are possible without any problems. The high cutting speed is an additional impressive advantage in this cutting process.
Abrasive waterjet cutting
Highest cutting performance for hard materials
In order to achieve a higher cutting performance for hard materials, a sharp-edged cutting sand (garnet sand, commonly also called abrasive sand) is added to the water jet.
Abrasive waterjet cutting is used for materials such as stone, glass, carbon, copper, steel, aluminum, brass, sheet metal, ceramics, plastics, and many others.
As a rule of thumb, the abrasive waterjet can cut materials up to the hardness of the abrasive sand used (Mohs hardness of approx. 8) and up to a thickness of approx. 300 mm.
What materials can be cut with waterjet cutting?
In short, almost all materials
The list of materials that can be cut with a waterjet is very long. A brief overview of the possible materials.
For more details on the applications, features, benefits, technical details and FAQs on the most commonly used materials, please visit the detail page for each material.
7 Advantages of waterjet cutting
An attractive choice for precise cutting
Waterjet cutting is a modern and extremely versatile cutting technique. It offers a number of impressive advantages that make it an attractive choice for accurate cutting of a wide variety of materials.
7 convincing properties of waterjet cutting stand out in particular.
Cutting quality
The cutting speed has the most significant influence on quality and costs. The faster you cut with the waterjet, the rougher the cut. Likewise, the working pressure or feed rate and the material resistance or material thickness play a major role in the cutting quality
Depending on the cutting requirement, the greatest challenge is therefore to find the ideal compromise between the desired cutting quality and the fastest possible feed rate.
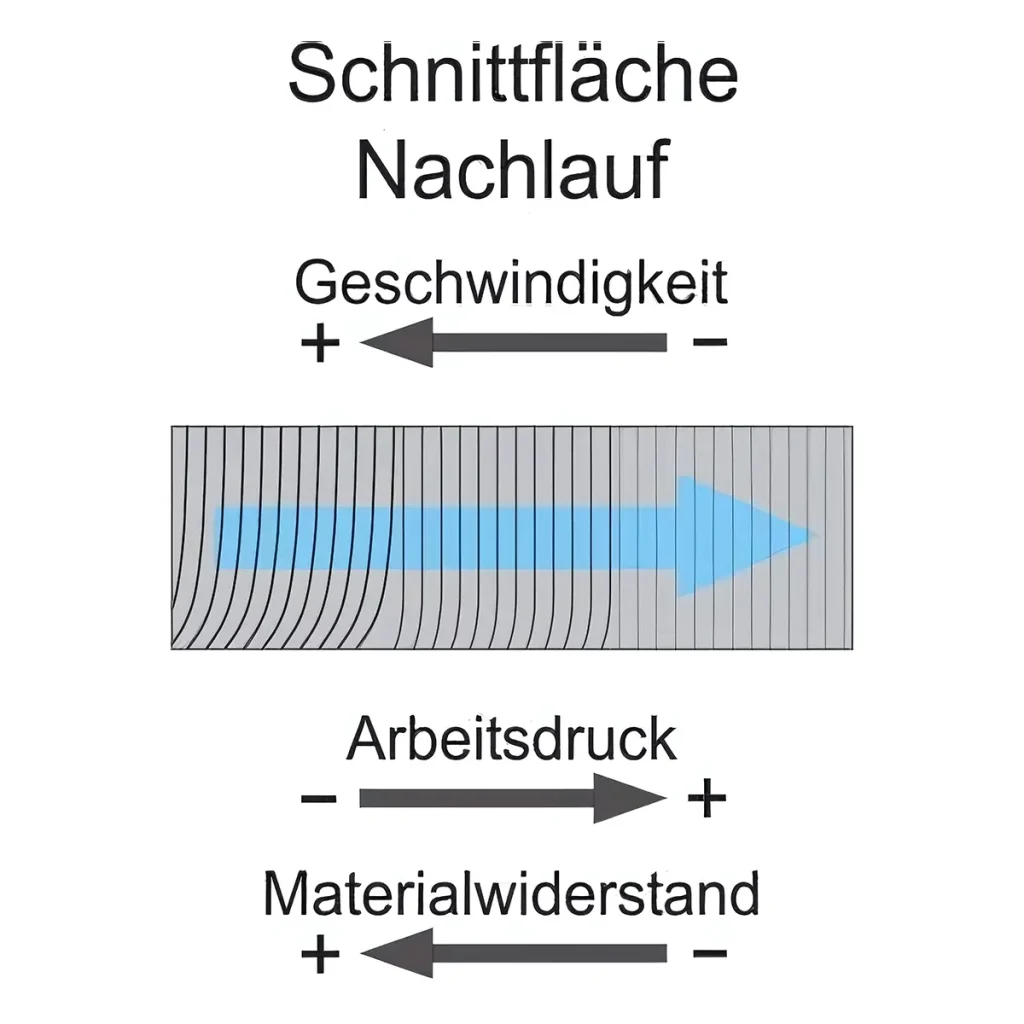
Feed
Cutting quality is mainly controlled directly by adjusting the feed rate. Basic parameters such as water pressure or sand quantity differ only minimally across manufacturers. However, it is important to consider the maximum cutting speed permitted by the technical design of various waterjet cutting systems.
Examples of feed rates for cut quality level Q3 – standard cut:
| Material | Cutting speed | Material thickness |
|---|---|---|
| (Stainless) Steel | 200 mm/min | 10 mm |
| Aluminum | 600 mm/min | 10 mm |
| Granite | 100 mm/min | 50 mm |
| Material | Cutting speed | Material thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | 1400 mm/min | 10 mm |
| Carbon | 1000 mm/min | 10 mm |
| Copper | 400 mm/min | 10 mm |

Standards
In the field of thermal cutting technologies, there are many accompanying standards, but for waterjet cutting , there are few corresponding specifications.
In Switzerland, there is SN 214001: 2010 – “Non-contact cutting – Waterjet cutting – Geometric product specification and quality” – a standard that is also often used as a basis in Germany and Austria.
SN 214001 describes 5 different quality levels, defines cutting angle errors, form and position deviations, contour errors and roughness.
Quality levels
The quality of waterjet cuts are classified into 5 quality levels as is customary in the industry. A distinction is made between separation cut (Q1), rough cut (Q2), standard cut (Q3), quality cut (Q4) and fine cut (Q5).
Basically, the difference between, for example, quality cut (Q4) and cut-off cut (Q1) is 3 times the speed and thus also 3 times the cost.

Q1
Separating cut

Q3
Standard cut

Q5
Fine cut
How expensive is waterjet cutting?
The cost of waterjet cutting depends on several factors. The main factors are the type of material, material thickness, complexity of the design and machine settings.
There are also other individual factors, such as the location (cost of electricity & water), possible cutting speeds (depending on the material & the material thickness, pressure, etc.) and necessary preparatory work (e.g. data transfer, material preparations, etc.).
The best way is to tell us your requirements and we will offer you a customized solution. Feel free to contact us or request a test cut with your material.
Main factors
- Material type
- Material thickness
- Design complexity
- Machine configurations
Individual factors
- Site costs
- Cutting speeds
- Preparatory work
Operating costs
Operational costs in waterjet cutting are largely composed of energy costs and wear part/maintenance costs. In abrasive waterjet cutting, the abrasive and its disposal is the proportionally largest cost factor.
Pure water cutting
Abrasive waterjet cutting
Sample cost breakdown
| Pumpentyp | Antriebsleistung (kW) | Betriebsdruck (bar) | Düsendurchmesser (mm) | Max. Schnittleistung lfm/h | Kosten pro Laufmeter €/lfm | Verschleißteilkosten €/h | Stromkosten €/h | Gesamtkosten bei max. Schnittleistung |
| Konventionell | 11 | 4000 | 0,2 | 12 | € 0,97 | € 2,50 | € 1,60 | € 15,74 |
| Konventionell | 19 | 4000 | 0,25 | 16,8 | € 0,90 | € 2,30 | € 2,70 | € 20,12 |
| Konventionell | 37 | 4000 | 0,35 | 33 | € 0,63 | € 2,50 | € 5,30 | € 28,59 |
| Servoantrieb | 37 | 4000 | 0,35 | 33 | € 0,63 | € 2,30 | € 4,50 | € 27,59 |
| Servoantrieb | 45 | 4000 | 0,4 | 42 | € 0,58 | € 2,30 | € 5,60 | € 32,26 |
| Konventionell | 75 | 4000 | 0,5 | 55,8 | € 0,61 | € 5,00 | € 10,50 | € 49,54 |
| Ultrahochdruck | 45 | 6000 | 0,25 | 47,4 | € 0,60 | € 8,00 | € 6,60 | € 43,04 |
| Ultrahochdruck | 75 | 6000 | 0,35 | 71,4 | € 0,60 | € 16,00 | € 10,20 | € 69,04 |
Example based on the material steel with a material thickness of 5mm.
All values in relation to mean cutting quality Q3. All data are approximate values without guarantee. All information is to be verified individually.
Waterjet cutting as a favorable alternative
Waterjet cutting is a favorable alternative due to its material diversity, which often eliminates the need for separate processing machines. Sensitive materials such as glass or ceramics, which could be damaged by other cutting methods, can also be cut gently.
The low heat influence, deformation or loss of hardness can be avoided. Complex shapes can be cut, precisely and quickly. Despite these many advantages, no toxic fumes or gases are produced, making waterjet cutting one of the most environmentally friendly cutting processes.
References
The best advertising is known to be satisfied customers
Among our references you will find customers & partners from various fields. Among them are companies from the following sectors:
- Metal industry
- Stone / Ceramics / Glass
- Plastics / foam industry
- Sealing industry
- Prototype / plant engineering
- Microwaterjet
- Educational Institutions
- Research
- Special materials
Perfectly tailored to your needs.
Waterjet cutting systems from STM
STM systems are divided into the EcoCut, MasterCut, PremiumCut, PremiumCut IFC, Cube and MicroCut product series and differ basically in size and equipment. Based on these equipment profiles, STM can configure a customized system for any requirement – from simple two-dimensional cuts to tube cutting to nested three-dimensional cuts.